Choice
Use choice lists to present a list of choices where buyers can make a single selection or multiple selections.
Anchor to choicelistpropsChoiceListProps
- Anchor to namenamestringrequired
A unique identifier for the field in the closest
Formcomponent.- Anchor to onChangeonChange(value: T) => voidrequired
A callback that is run whenever the choice list is changed. This callback is called with a string or array of strings indicating the ids of choices that should now be selected. This component is controlled, so you must store this value in state and reflect it back in the
valueprop.- Anchor to valuevalueTrequired
A
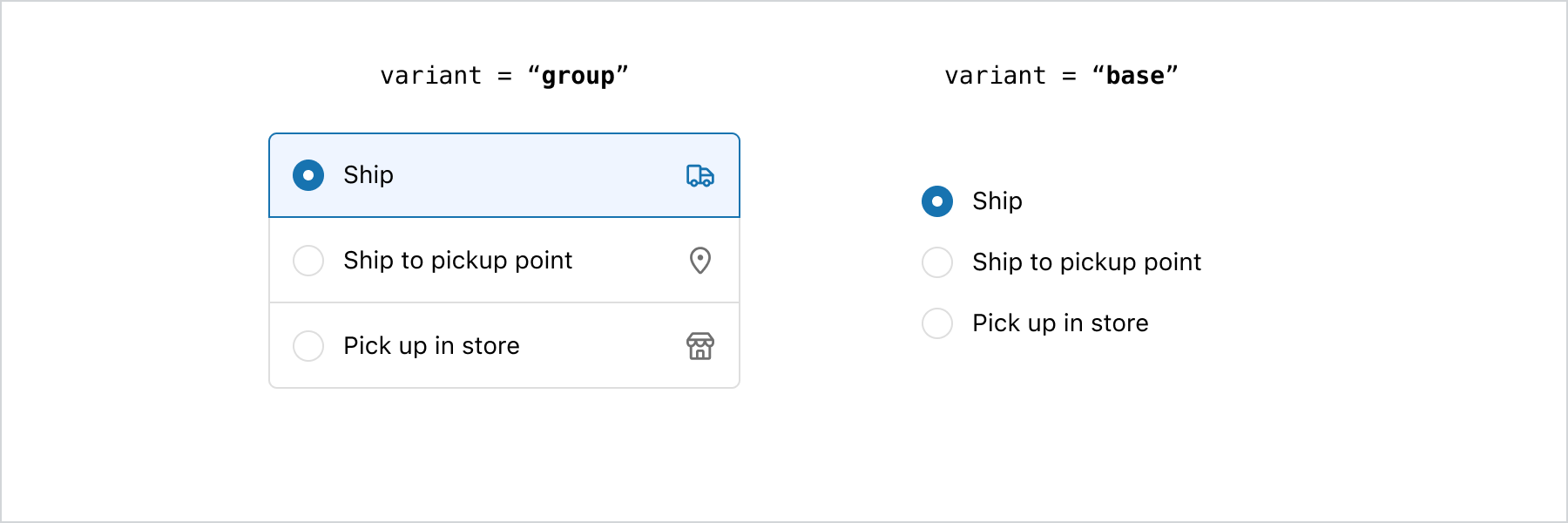
stringorstring[]indicating the ids of selected choices. When a string is set, choices render as radios. When a string array is set, choices render as checkboxes.- Anchor to variantvariant'base' | 'group'Default: 'base'
Toggle between
baseandgrouplook.Check the best practices to learn more about the variants.
Basic ChoiceList
Examples
Basic ChoiceList
React
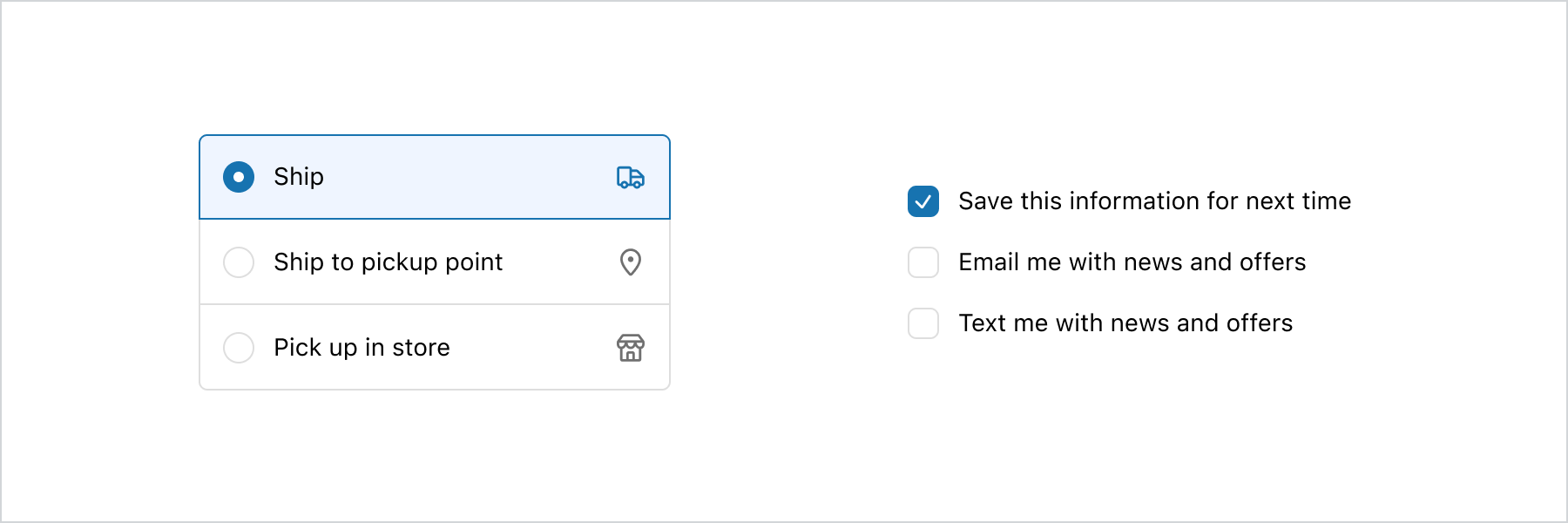
import { reactExtension, BlockStack, Choice, ChoiceList, Icon, InlineStack, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions-react/checkout'; export default reactExtension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', () => <Extension />, ); function Extension() { return ( <InlineStack> <ChoiceList name="group-single" variant="group" value="ship" onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <Choice secondaryContent={ <Icon source="truck" /> } id="ship" > Ship </Choice> <Choice secondaryContent={ <Icon source="marker" /> } id="ship-to-pickup-point" > Ship to pickup point </Choice> <Choice secondaryContent={ <Icon source="store" /> } id="pick-up" > Pick up in store </Choice> </ChoiceList> <ChoiceList name="base-multiple" value={['remember-me']} onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <BlockStack> <Choice id="remember-me"> Save this information for next time </Choice> <Choice id="email-me"> Email me with news and offers </Choice> <Choice id="text-me"> Text me with news and offers </Choice> </BlockStack> </ChoiceList> </InlineStack> ); }JS
import { extension, InlineStack, ChoiceList, Choice, BlockStack, Icon, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions/checkout'; export default extension('purchase.checkout.block.render', (root) => { const inlineStack = root.createComponent(InlineStack, undefined, [ root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'group-single', variant: 'group', value: 'ship', onChange: (value) => { console.log(`onChange event with value: ${value}`); }, }, [ root.createComponent( Choice, { secondaryContent: root.createComponent(Icon, {source: 'truck'}), id: 'ship', }, 'Ship', ), root.createComponent( Choice, { secondaryContent: root.createComponent(Icon, {source: 'marker'}), id: 'ship-to-pickup-point', }, 'Ship to pickup point', ), root.createComponent( Choice, { secondaryContent: root.createComponent(Icon, {source: 'store'}), id: 'pick-up', }, 'Pick up in store', ), ], ), root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'base-multiple', value: ['remember-me'], onChange: (value) => { console.log(`onChange event with value: ${value}`); }, }, [ root.createComponent(BlockStack, undefined, [ root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'remember-me'}, 'Save this information for next time', ), root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'email-me'}, 'Email me with news and offers', ), root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'text-me'}, 'Text me with news and offers', ), ]), ], ), ]); root.appendChild(inlineStack); });
Preview
Anchor to best-practicesBest Practices
Anchor to ContentContent
Include a title that either tells customers what to do or explains their available options.
Label options clearly based on what the option will do.
Avoid options that contradict each other when you’re allowing for multiple selections.
Anchor to Types of choicesTypes of choices
- The
basevariant is suitable for straightforward options, such as binary choices like 'yes' or 'no' answers. For simple options that require minimal visual emphasis, the base variant is the recommended choice. - The
groupvariant provides increased emphasis on choices through the use of colors, borders, and dividers. If the goal is to draw attention to the available options, the group variant is the ideal choice.
Anchor to Flexibility vs. cohesive experienceFlexibility vs. cohesive experience
- The
basevariant offers the flexibility to compose ChoiceLists with custom layouts, allowing for greater design composition possibilities. - Given the high level of flexibility offered by the
basevariant, prioritizing accessibility in the implementation is crucial. It is recommended to avoid using buttons or pressable components within the choices. - The
groupvariant adheres to a defined structure and provides excellent adaptability to align with the merchant’s brand. It is the ideal choice when strong cohesion with the merchant’s branding is required. Additionally, depending on the placement of the, Checkout will automatically update its appearance to seamlessly adapt to the surface it is on.
Anchor to Using detailsUsing details
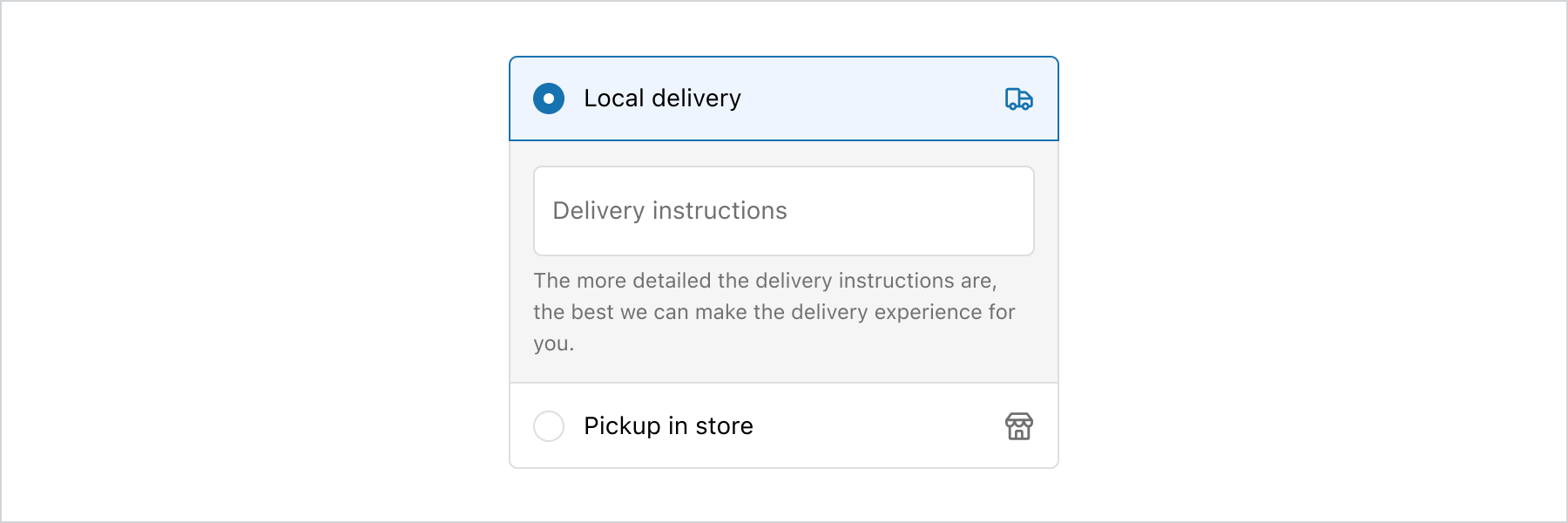
- The
detailsarea should be used only when additional input is required from the customer, specifically related to the choice they have made. - If the
detailsarea contains lengthy content, consider placing it outside of theto ensure that customers can easily digest the information.
Anchor to Long lists of optionsLong lists of options
- When faced with a considerable number of options, customers may feel overwhelmed, and it can consume valuable interface space. To address this, consider utilizing components like the Select component to condense options, or employ the Disclosure component to progressively reveal more choices upon customer request. Strategies such as paging, filtering, and searching can be employed to enhance usability.
Anchor to Clickable rowsClickable rows
- If an entire row needs to be clickable, utilize the
groupvariant, as it is specifically designed to enable clickable rows. In this scenario, the base variant may not provide the desired functionality, as only its content elements can be clicked, not the entire row. Attempting to use buttons or pressables to make an entire row clickable could lead to accessibility issues.
Anchor to examplesExamples
Anchor to example-custom-survey-using-the-base-variantCustom survey using the base variant
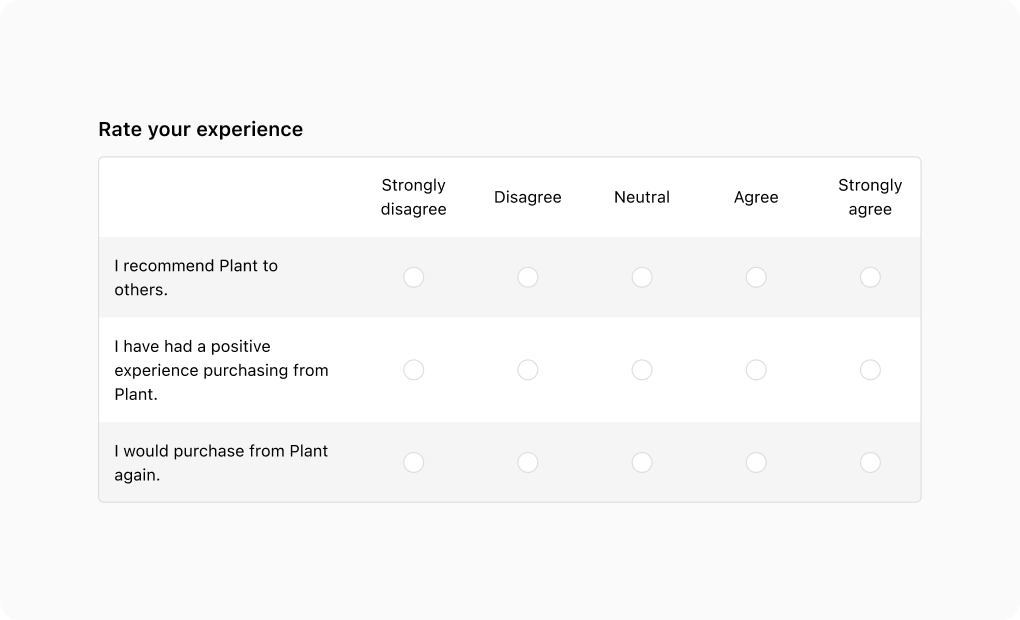
The base variant’s flexibility allows for the creation of Likert scales using the ChoiceList component. By utilizing layout components, you can easily structure rows and columns for this purpose.
Anchor to example-collecting-additional-informationCollecting additional information
The ChoiceList’s group variant, combined with the details property, allows for the conditional display of information when needed.
Anchor to example-displaying-a-short-list-of-time-choicesDisplaying a short list of time choices
The ChoiceList component is great for presenting a concise list of options, particularly when showcasing time ranges due to its ample horizontal space. However, if there’s more than 5 choices, use the Select component instead.
Custom survey using the base variant
Examples
Custom survey using the base variant
Description
The base variant’s flexibility allows for the creation of Likert scales using the ChoiceList component. By utilizing layout components, you can easily structure rows and columns for this purpose.
React
import { reactExtension, Choice, ChoiceList, Grid, TextBlock, View, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions-react/checkout'; export default reactExtension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', () => <Extension />, ); function Extension() { return ( <Grid columns={[ 'fill', '13%', '13%', '13%', '13%', '13%', ]} rows="auto" spacing="none" border="base" cornerRadius="base" overflow="hidden" > <View /> <View padding={['tight', 'extraTight']} blockAlignment="center" accessibilityVisibility="hidden" > <TextBlock inlineAlignment="center"> Strongly disagree </TextBlock> </View> <View padding={['tight', 'extraTight']} blockAlignment="center" accessibilityVisibility="hidden" > <TextBlock inlineAlignment="center"> Disagree </TextBlock> </View> <View padding={['tight', 'extraTight']} blockAlignment="center" accessibilityVisibility="hidden" > <TextBlock inlineAlignment="center"> Neutral </TextBlock> </View> <View padding={['tight', 'extraTight']} blockAlignment="center" accessibilityVisibility="hidden" > <TextBlock inlineAlignment="center"> Agree </TextBlock> </View> <View padding={['tight', 'extraTight']} blockAlignment="center" accessibilityVisibility="hidden" > <TextBlock inlineAlignment="center"> Strongly agree </TextBlock> </View> <ChoiceList name="question1" value="" onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <View background="subdued" padding="base" blockAlignment="center" > <TextBlock> I recommend Plant to others. </TextBlock> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question1-1" accessibilityLabel="Strongly disagree" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question1-2" accessibilityLabel="Disagree" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question1-3" accessibilityLabel="Neutral" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question1-4" accessibilityLabel="Agree" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question1-5" accessibilityLabel="Strongly agree" /> </View> </ChoiceList> <ChoiceList name="question2" value="" onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <View padding="base" blockAlignment="center" > <TextBlock> I have had a positive experience purchasing from Plant. </TextBlock> </View> <View blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question2-1" accessibilityLabel="Strongly disagree" /> </View> <View blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question2-2" accessibilityLabel="Disagree" /> </View> <View blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question2-3" accessibilityLabel="Neutral" /> </View> <View blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question2-4" accessibilityLabel="Agree" /> </View> <View blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question2-5" accessibilityLabel="Strongly agree" /> </View> </ChoiceList> <ChoiceList name="question3" value="" onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <View background="subdued" padding="base" blockAlignment="center" > <TextBlock> I would purchase from Plant again. </TextBlock> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question3-1" accessibilityLabel="Strongly disagree" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question3-2" accessibilityLabel="Disagree" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question3-3" accessibilityLabel="Neutral" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question3-4" accessibilityLabel="Agree" /> </View> <View background="subdued" blockAlignment="center" inlineAlignment="center" > <Choice id="question3-5" accessibilityLabel="Strongly agree" /> </View> </ChoiceList> </Grid> ); }JavaScript
import { extension, Choice, ChoiceList, Grid, TextBlock, View, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions/checkout'; export default extension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', (root) => { const grid = root.createComponent( Grid, { columns: [ 'fill', '13%', '13%', '13%', '13%', '13%', ], rows: 'auto', spacing: 'none', border: 'base', cornerRadius: 'base', overflow: 'hidden', }, [ root.createComponent(View, {}, []), root.createComponent( View, { padding: ['tight', 'extraTight'], blockAlignment: 'center', accessibilityVisibility: 'hidden', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {inlineAlignment: 'center'}, 'Strongly disagree', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { padding: ['tight', 'extraTight'], blockAlignment: 'center', accessibilityVisibility: 'hidden', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {inlineAlignment: 'center'}, 'Disagree', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { padding: ['tight', 'extraTight'], blockAlignment: 'center', accessibilityVisibility: 'hidden', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {inlineAlignment: 'center'}, 'Neutral', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { padding: ['tight', 'extraTight'], blockAlignment: 'center', accessibilityVisibility: 'hidden', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {inlineAlignment: 'center'}, 'Agree', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { padding: ['tight', 'extraTight'], blockAlignment: 'center', accessibilityVisibility: 'hidden', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {inlineAlignment: 'center'}, 'Strongly agree', ), ), // Then create the ChoiceList for 'question1' root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'question1', value: '', onChange: (value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }, }, [ root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', padding: 'base', blockAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {}, 'I recommend Plant to others.', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question1-1', accessibilityLabel: 'Strongly disagree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question1-2', accessibilityLabel: 'Disagree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question1-3', accessibilityLabel: 'Neutral', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question1-4', accessibilityLabel: 'Agree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question1-5', accessibilityLabel: 'Strongly agree', }), ), ], ), // Then create the ChoiceList for 'question2' root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'question2', value: '', onChange: (value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }, }, [ root.createComponent( View, { padding: 'base', blockAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {}, 'I have had a positive experience purchasing from Plant.', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question2-1', accessibilityLabel: 'Strongly disagree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question2-2', accessibilityLabel: 'Disagree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question2-3', accessibilityLabel: 'Neutral', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question2-4', accessibilityLabel: 'Agree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question2-5', accessibilityLabel: 'Strongly agree', }), ), ], ), // Then create the ChoiceList for 'question3' root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'question3', value: '', onChange: (value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }, }, [ root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', padding: 'base', blockAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent( TextBlock, {}, 'I would purchase from Plant again.', ), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question3-1', accessibilityLabel: 'Strongly disagree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question3-2', accessibilityLabel: 'Disagree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question3-3', accessibilityLabel: 'Neutral', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question3-4', accessibilityLabel: 'Agree', }), ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'subdued', blockAlignment: 'center', inlineAlignment: 'center', }, root.createComponent(Choice, { id: 'question3-5', accessibilityLabel: 'Strongly agree', }), ), ], ), ], ); root.appendChild(grid); }, );Collecting additional information
Description
The ChoiceList’s group variant, combined with the details property, allows for the conditional display of information when needed.
React
import { reactExtension, BlockStack, Choice, ChoiceList, DatePicker, TextBlock, TextField, View, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions-react/checkout'; export default reactExtension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', () => <Extension />, ); function Extension() { return ( <ChoiceList variant="group" name="white-glove" value={['white-glove-1']} onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <Choice id="white-glove-1" details={ <> <BlockStack spacing="base"> <BlockStack spacing="extraTight"> <TextBlock> Choose a delivery date </TextBlock> <View background="base" border="base" cornerRadius="base" padding="base" > <DatePicker selected="" /> </View> </BlockStack> <BlockStack spacing="extraTight"> <TextField label="Additional instructions" value="" /> <TextBlock appearance="subdued" size="small" > The more detailed the delivery instructions are, the best we can make the delivery experience for you. </TextBlock> </BlockStack> </BlockStack> </> } > Use white glove delivery service </Choice> </ChoiceList> ); }JavaScript
import { extension, BlockStack, Choice, ChoiceList, DatePicker, TextBlock, TextField, View, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions/checkout'; export default extension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', (root) => { const choiceList = root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'white-glove', value: ['white-glove-1'], onChange: (nextValue) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${nextValue}`, ); }, }, [ root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'white-glove-1'}, [ root.createComponent( BlockStack, {spacing: 'base'}, [ root.createComponent( BlockStack, {spacing: 'extraTight'}, [ root.createComponent( TextBlock, {}, 'Choose a delivery date', ), root.createComponent( View, { background: 'base', border: 'base', cornerRadius: 'base', padding: 'base', }, root.createComponent( DatePicker, {selected: ''}, ), ), ], ), root.createComponent( BlockStack, {spacing: 'extraTight'}, [ root.createComponent( TextField, { label: 'Additional instructions', value: '', }, ), root.createComponent( TextBlock, { appearance: 'subdued', size: 'small', }, 'The more detailed the delivery instructions are, the best we can make the delivery experience for you.', ), ], ), ], ), ], ), ], ); root.appendChild(choiceList); }, );Displaying a short list of time choices
Description
The ChoiceList component is great for presenting a concise list of options, particularly when showcasing time ranges due to its ample horizontal space. However, if there’s more than 5 choices, use the [Select](/docs/api/checkout-ui-extensions/components/forms/select) component instead.
React
import { reactExtension, BlockStack, ChoiceList, Choice, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions-react/checkout'; export default reactExtension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', () => <Extension />, ); function Extension() { return ( <ChoiceList name="time" value="" onChange={(value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }} > <BlockStack> <Choice id="morning"> 9:00 AM - 12:00 PM </Choice> <Choice id="afternoon"> 12:00 PM - 3:00 PM </Choice> <Choice id="evening"> 3:00 PM - 5:00 PM </Choice> </BlockStack> </ChoiceList> ); }JavaScript
import { extension, BlockStack, ChoiceList, Choice, } from '@shopify/ui-extensions/checkout'; export default extension( 'purchase.checkout.block.render', (root) => { const choiceList = root.createComponent( ChoiceList, { name: 'time', value: '', onChange: (value) => { console.log( `onChange event with value: ${value}`, ); }, }, [ root.createComponent(BlockStack, {}, [ root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'morning'}, '9:00 AM - 12:00 PM', ), root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'afternoon'}, '12:00 PM - 3:00 PM', ), root.createComponent( Choice, {id: 'evening'}, '3:00 PM - 5:00 PM', ), ]), ], ); root.appendChild(choiceList); }, );
Preview