Authenticate payments with 3D Secure
On September 14, 2019, the Revised Payment Service Directive, also known as PSD2, was implemented in all countries in the European Economic Area (EEA). PSD2 requires most online transactions within the EEA to have customer authentication. To be compliant, Shopify processes credit card transactions in the EEA by using 3D Secure, which is a payment authentication method.
This guide describes the 3D Secure authentication process and how to update your sales channel app so that it supports payment authentication by using 3D Secure. The mutations in this tutorial that complete checkouts are available only for sales channels.
Requirements
Anchor link to section titled "Requirements"- You've completed the Getting started with the Storefront API guide.
You're familiar with querying products and collections.
If instead of completing the Getting started, you've turned your app into a sales channel and requested and been approved for payment processing.
You've familiarized yourself with the concept of payment authentication with 3D Secure
Payment authentication workflow
Anchor link to section titled "Payment authentication workflow"The following diagram shows the general workflow that you can follow to authenticate payments that require 3D Secure authentication.
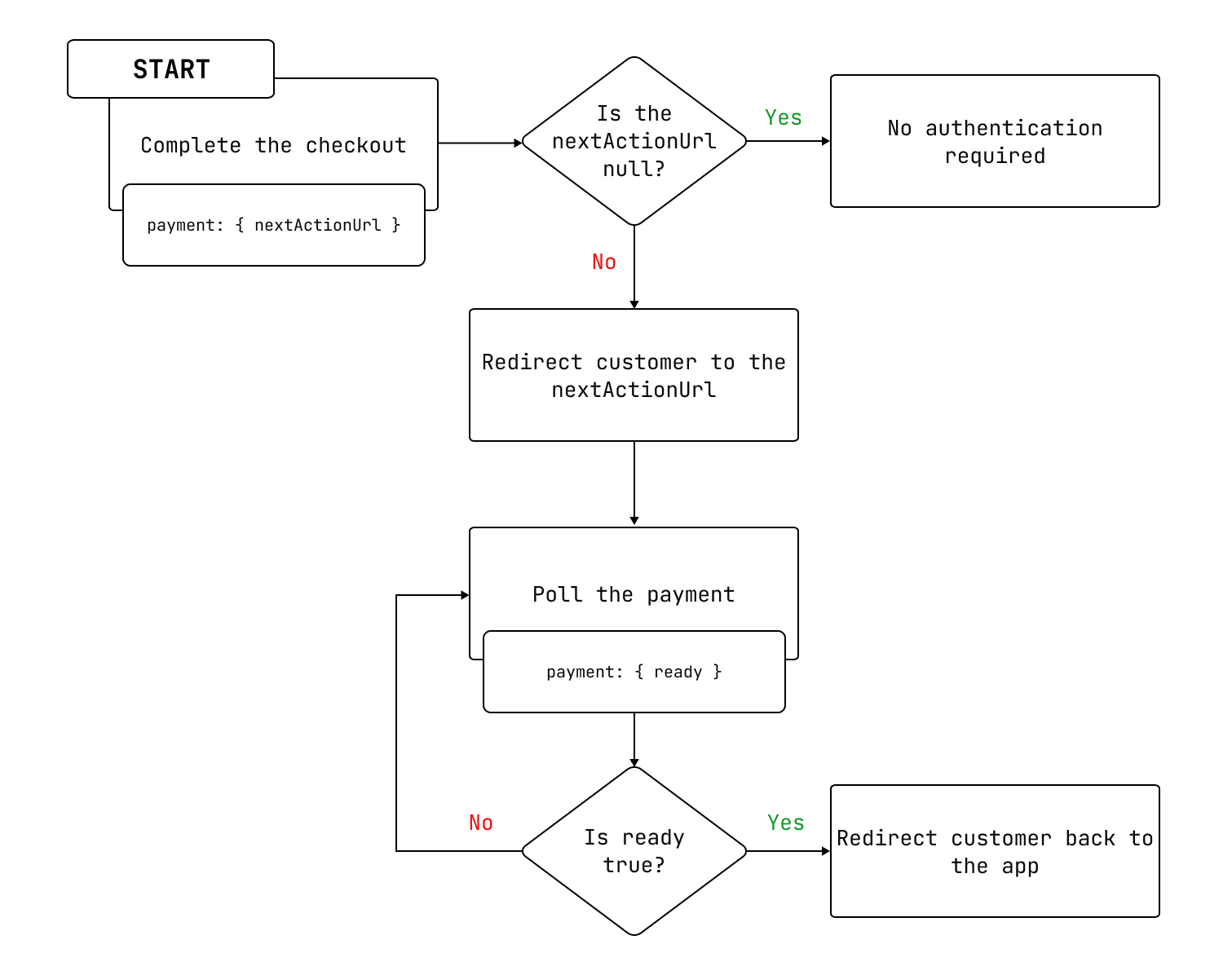
- The app completes the checkout and receives the
nextActionUrlattribute of thePaymentobject. If the
nextActionUrlisnull, then the customer doesn't require authentication.If the
nextActionUrlisn'tnull, then the app redirects the customer to thenextActionUrlto complete authentication.The app polls the payment until
readyreturnstrue.The app redirects the customer back to the app.
Step 1: Complete the checkout
Anchor link to section titled "Step 1: Complete the checkout"You can pass the checkout ID, payment information, and session ID to the checkoutCompleteWithCreditCardV2 mutation to complete a checkout. For more information about creating and completing a checkout, refer to Create a checkout with the Storefront API.
The following example shows a request and response for the checkoutCompleteWithCreditCardV2 mutation. Make note of the nextActionUrl in the response, which you'll use to poll the payment in the next step.
Step 2: Redirect the customer
Anchor link to section titled "Step 2: Redirect the customer"The nextActionUrl field contains the URL where the customer needs to be redirected so they can complete the 3D Secure payment flow. Your app needs to send the customer to this URL so that they can authenticate their payment.
If the nextActionUrl is null, then the customer doesn't need to authenticate their payment.
Step 3: Poll the payment
Anchor link to section titled "Step 3: Poll the payment"After you've sent your customer to the nextActionUrl, your app needs to poll the payment. The Payment object includes the ready field, which is a Boolean that indicates whether the payment is still processing asynchronously. The ready field remains false until authentication is completed with either a success or failure.
Your app should continue to poll the payment until the ready field returns true. When ready is true, the payment has reached a final state and nothing further will change. At this point, the completedAt field on the checkout returns a time for a successful payment, or null for a payment that fails to complete. If the payment fails, then an error message is returned.
The following example shows how to poll a payment, which informs you if the payment has completed processing:
Step 4: Redirect the customer back to the app
Anchor link to section titled "Step 4: Redirect the customer back to the app"After the authentication is completed, the customer is redirected to a processing page. Your app is responsible for closing the page or webview after the authentication is completed and redirecting the customer back to your app.
Handling payments that don't require 3D Secure
Anchor link to section titled "Handling payments that don't require 3D Secure"For payments that don't require 3D Secure, there aren't any changes to the app or sales channel’s behavior:
nextActionUrlalways returnsnull. If you continue to poll the token, then thereadyfield eventually returnstruewhen the payment has completed its asynchronous processing.- If the payment succeeds, then the checkout's
completedAtfield is updated with the time of completion. - If the payment fails, then the checkout's
completedAtfield remainsnull, anderrorMessagecontains a payment processing error message.
Handling API timeouts for 3D Secure
Anchor link to section titled "Handling API timeouts for 3D Secure"If the Payment object includes a nextActionUrl field, but doesn't handle the redirect within ten minutes, then Shopify marks the authentication as an error, and returns an error message.